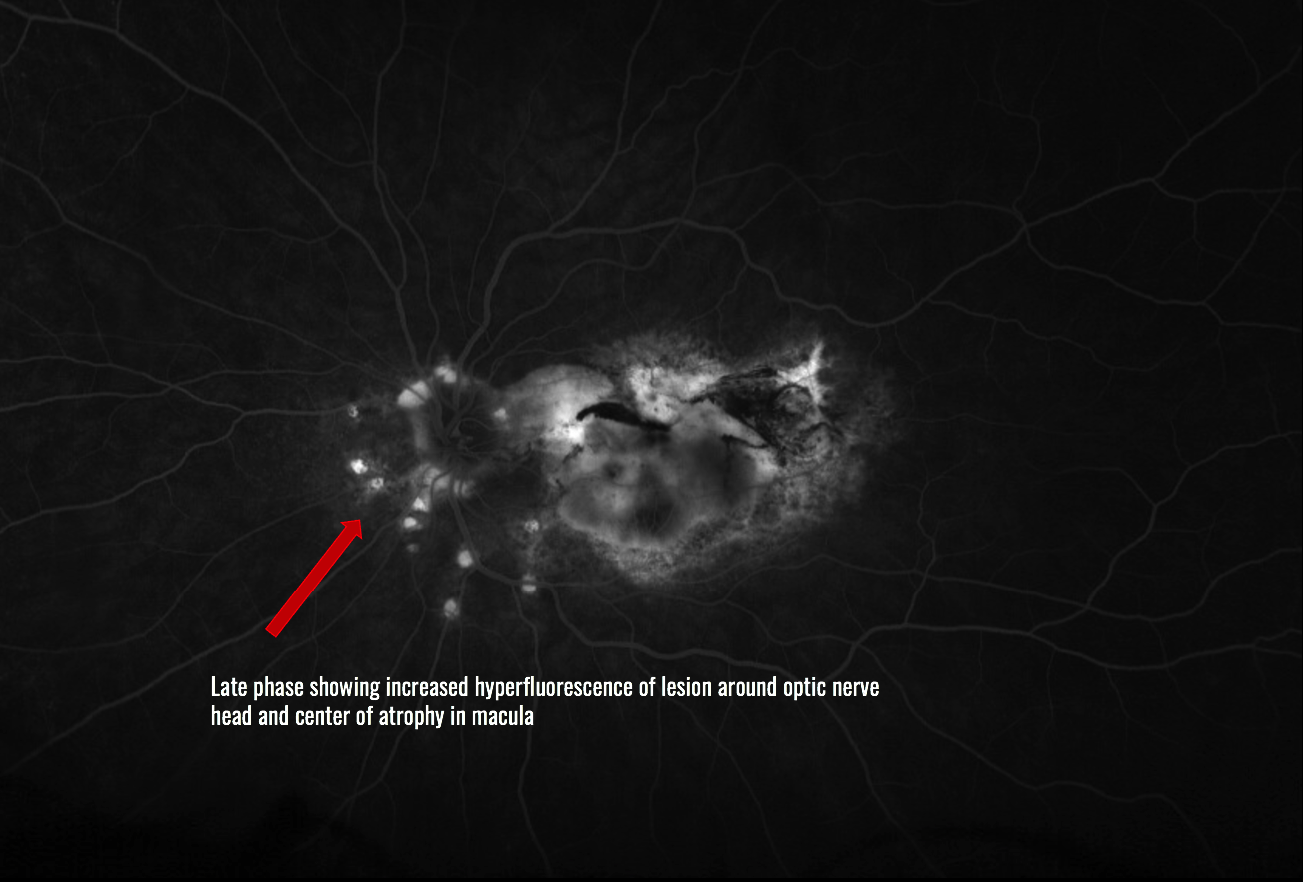
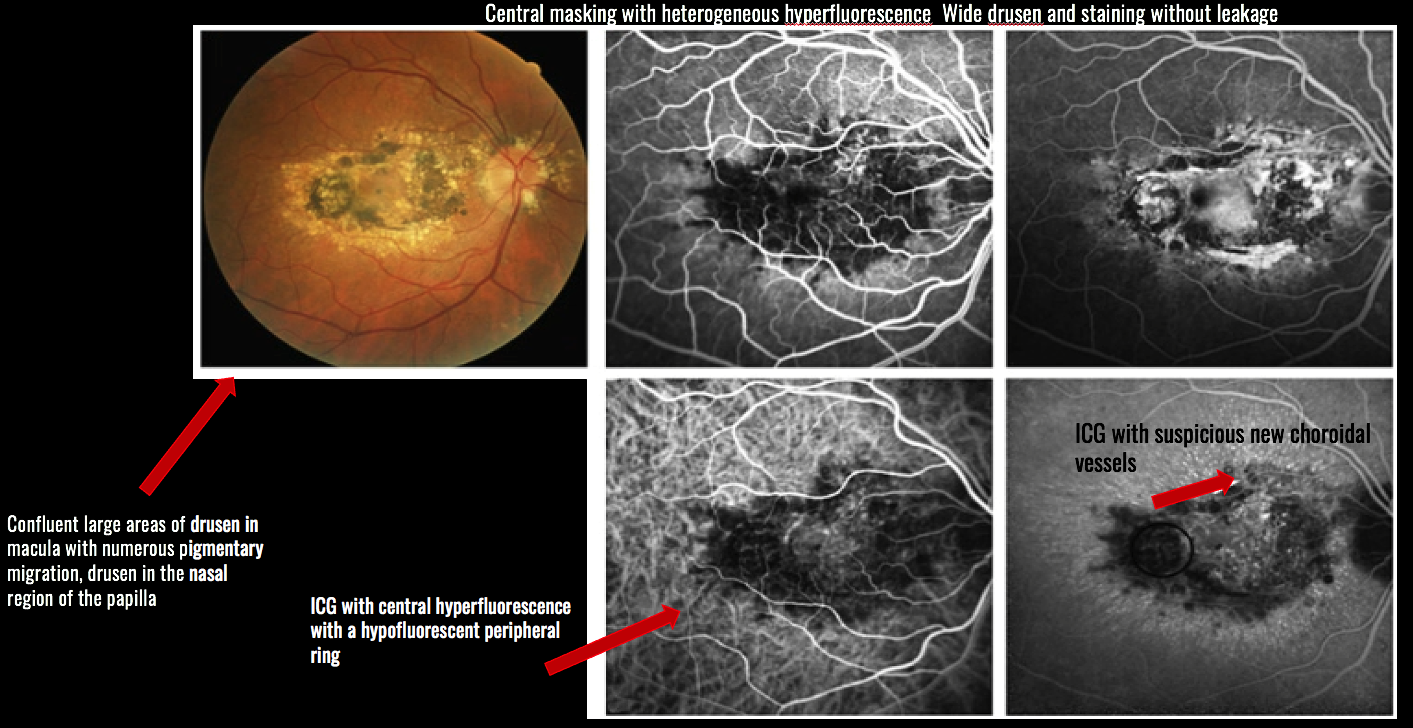
CASE OF THE MONTH: April 2023
Sweet Switzerland


Case:
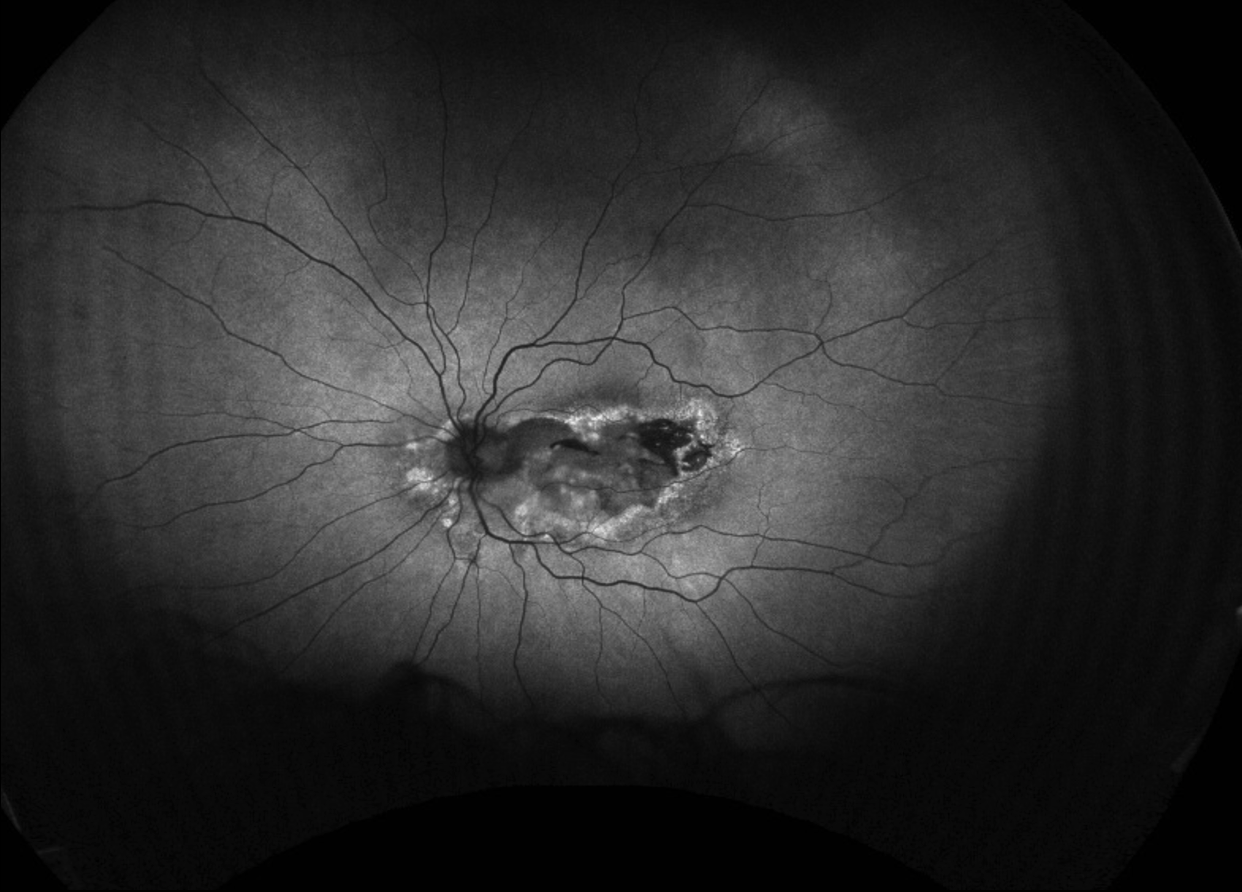
68-year-old woman presented with decreased central vision in both eyes for many years
History:
- Past ocular history: “Dry AMD”
- Family ocular history: “AMD” in many family members
- Past medical history: Breast cancer (1997-2012) s/p mastectomy in 1998, COPD
- Social history: Denied ETOH, illicit drug use, or smoking
- Medications: Letrozole, albuterol inhaler
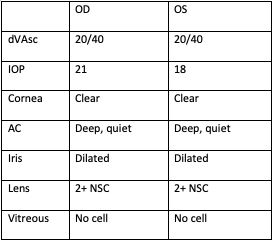
Exam:
Differential diagnosis:
- Doyne Honeycomb retinal dystrophy
- Age related macular degeneration
- Pattern dystrophies
- Best disease
- Stargardt's disease
- Sorsby fundus dystrophy
Genetic testing results:
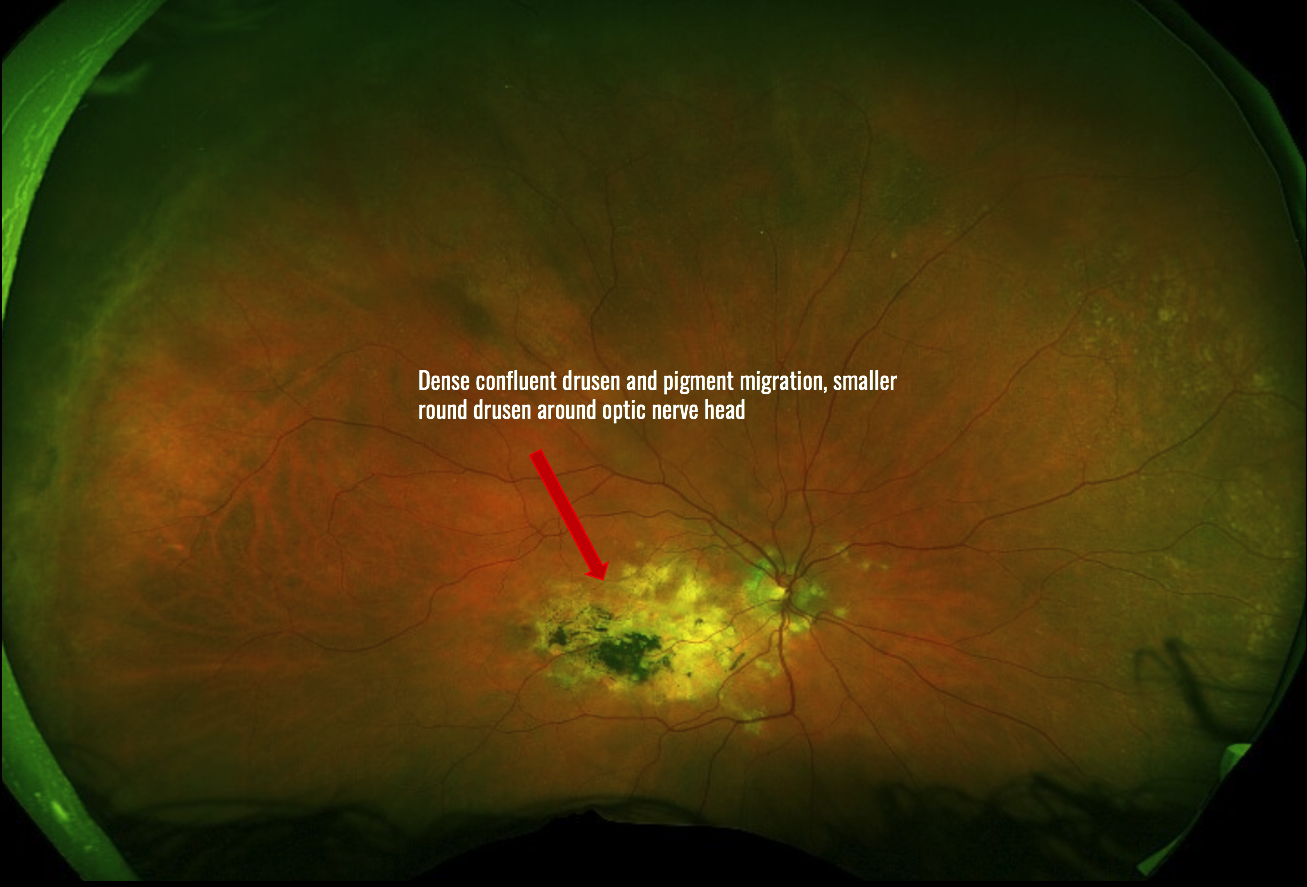
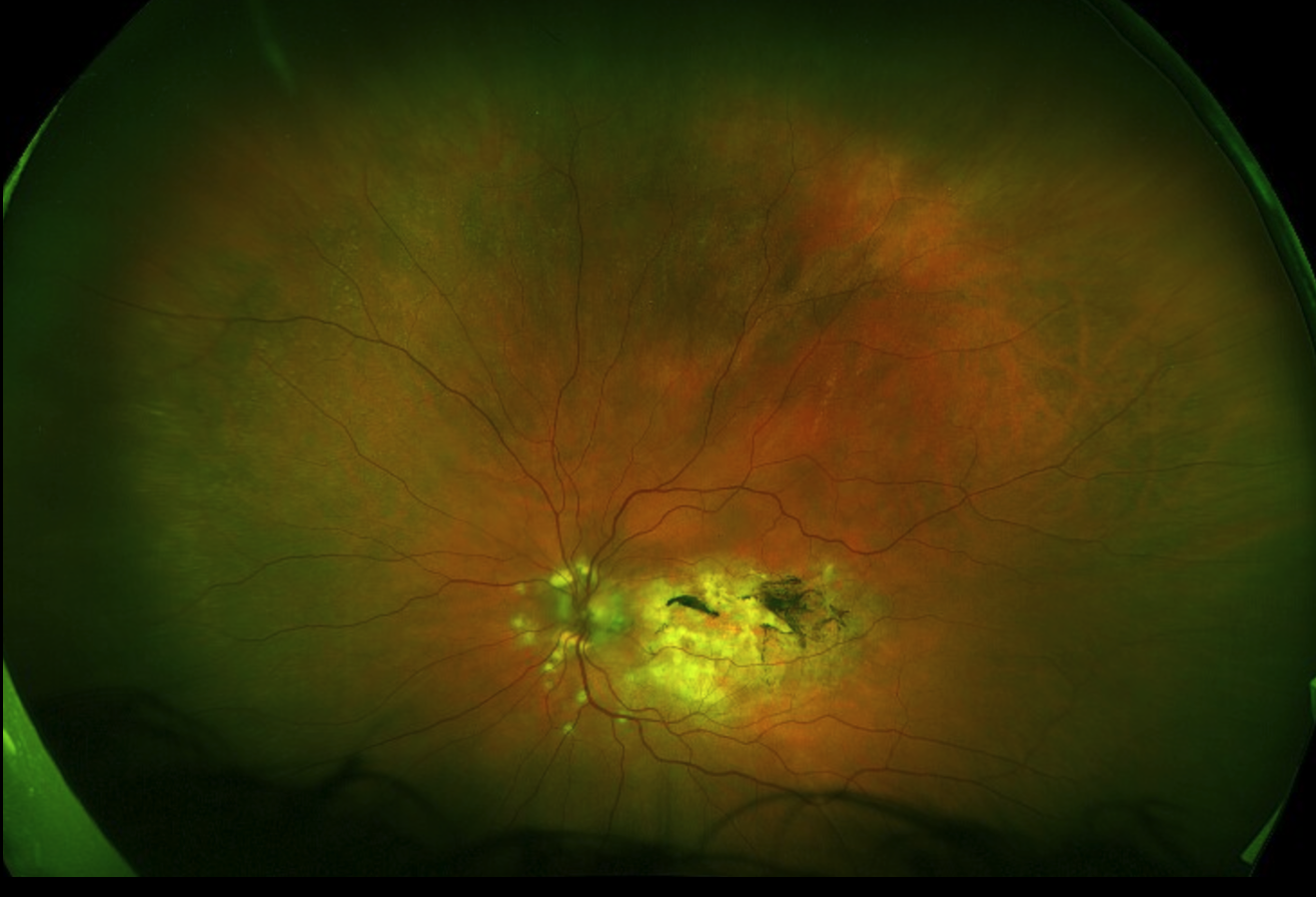
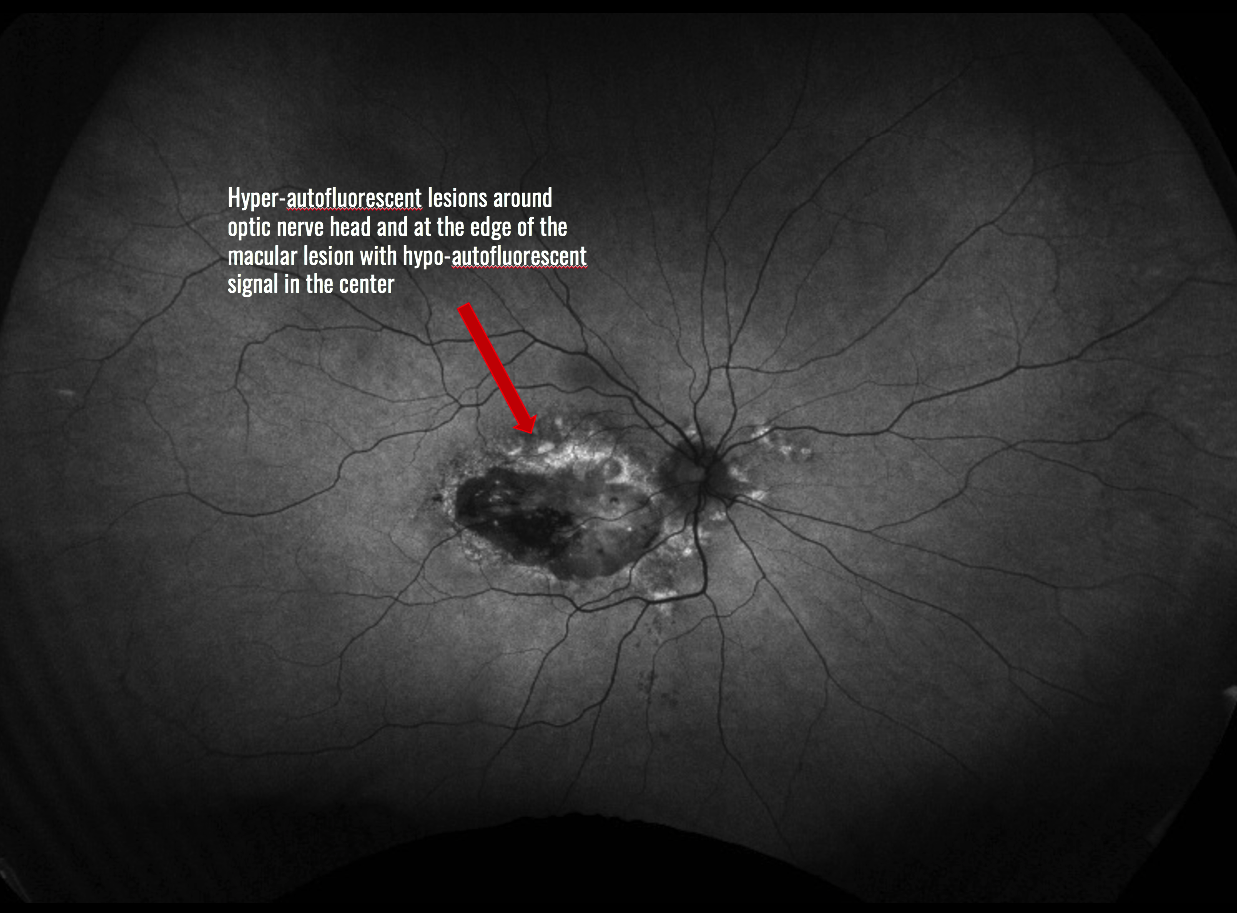
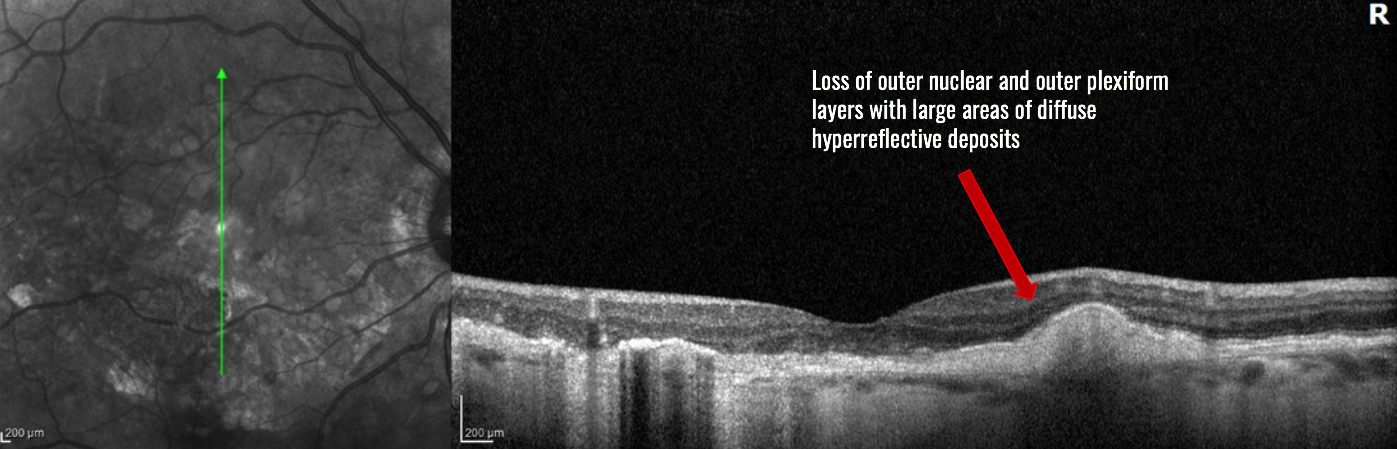
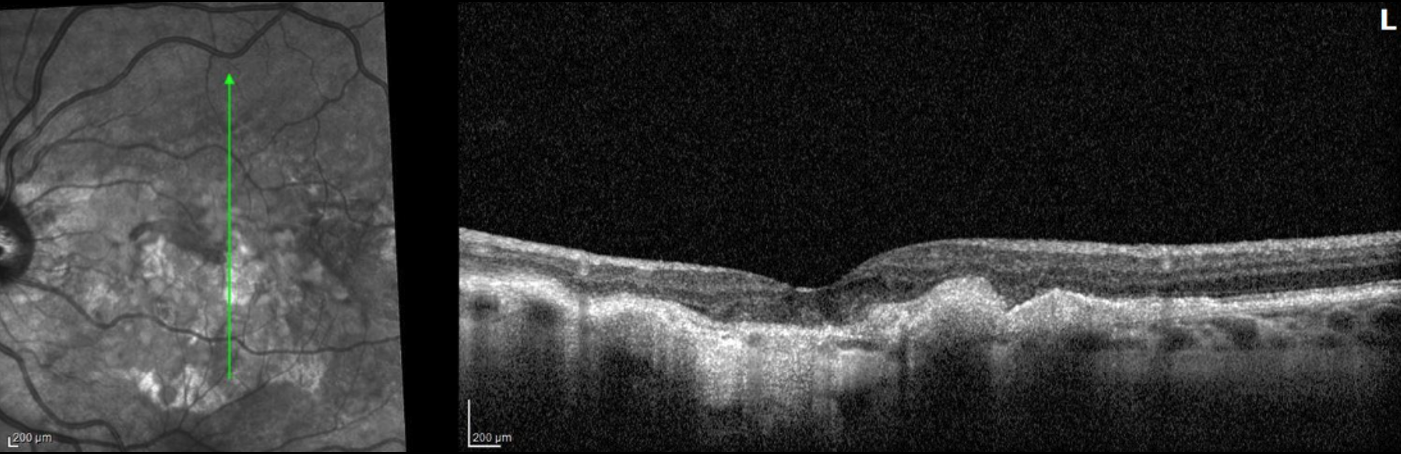
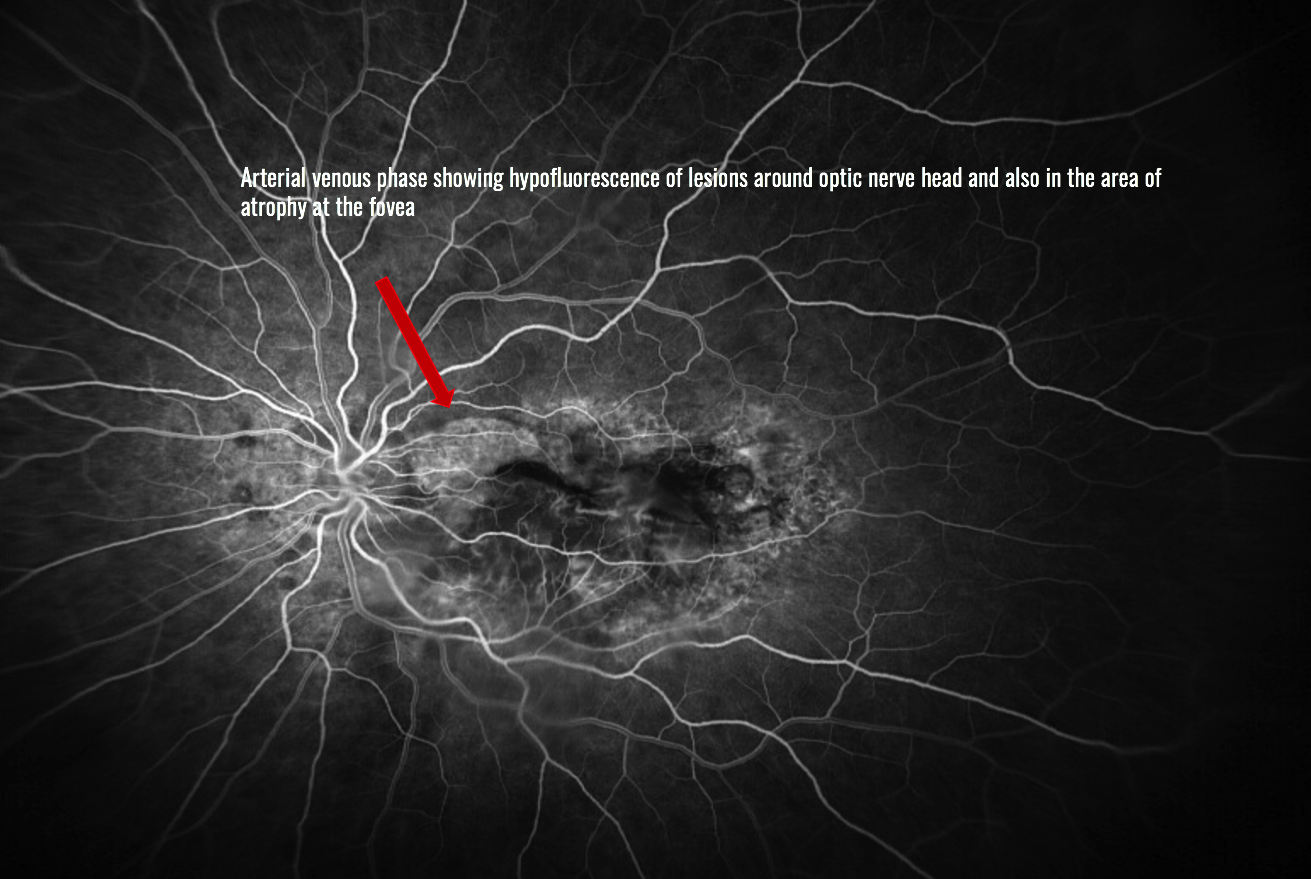
Diagnosis: Doyne Honeycomb Dystrophy (Malattia Leventinese)
Doyne Honeycomb Retinal Dystrophy (DHRD)
- DHRD was first reported by Doyne in 1899
- Was also described in Switzerland (Levantine Valley) in 1925 as Malattia Leventinese
- AD progressive retinal disease
- A single missense mutation in the EGF gene containing EFEMP1 protein
- Pts present with vision loss, metamorphopsia, and paracentral scotomas in mid adulthood (40-50 years of age)
- Complications of secondary choroidal neovascularization and hemorrhage can lead to progression of this condition
Sheyanth IN, Lolas IB, Okkels H, Kiruparajan LP, Abildgaard SK, Petersen MB. First reported case of Doyne honeycomb retinal dystrophy (Malattia Leventinese/autosomal dominant drusen) in Scandinavia. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2021;9(4):e1652.
Serra R, Coscas F, Messaoudi N, Srour M, Souied E. Choroidal Neovascularization in Malattia Leventinese Diagnosed Using Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography. Am J Ophthalmol. 2017;176:108-117.
Zhang K, Sun X, Chen Y, et al. Doyne honeycomb retinal dystrophy/malattia leventinese induced by EFEMP1 mutation in a Chinese family. BMC Ophthalmol. 2018;18(1):318.
Doyne Honeycomb Retinal Dystrophy (DHRD)
- Anti-VEGF if needed for CNV